History of gasoline direct injection
History of fuel direct injection systems
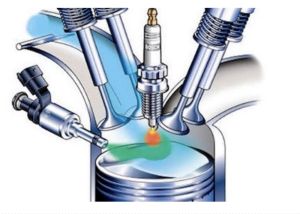
Since the inception of the first internal combustion engines, engineers and inventors have tried to improve the design and increase engine parameters such as power and fuel consumption. In the beginning, simple carburettor systems appeared that became more and more elaborate over time. The next breakthrough was the use of indirect injection, first mechanical, then electronic. So far, the most advanced type of fueling for a gasoline engine is direct injection. But maybe a little history of how it happened.
The first application of gasoline direct injection was the Hesselman engine, invented by the Swedish engineer Jonas Hesselman in 1925. The Hesselman engine used a lean fuel mixture and injected fuel at the end of the compression stroke which was then ignited with a spark plug. After warming up, the engine was switched to diesel or kerosene. The Hesselman engine had a low compression ratio and was designed to run on heavy fuel oils.
Gasoline direct injection was also used in aircraft during World War II. In the German Junkers Jumo 210, the Daimler-Benz DB 601, both 1937, and the Soviet Shvetsov ASH-82 FN, 1943, as well as the American Wright R-3350, 1944. The first automotive direct injection system was developed by Bosch and was developed by Goliath and Gutbrod in 1952 and a 1955 Mercedes-Benz 300SL. It was the first car with serial direct fuel injection. Bosch fuel injectors were placed in holes on the cylinder wall in place of the spark plugs, and the plugs were moved to the cylinder head. Later, due to the high cost, indirect fuel injection became widely used.
In the early 1970s, research was conducted with the support of the American Motors Corporation (AMC) to develop Direct Fuel Injection (SCFI). The conventional AMC combustion engine has been revised and a redesigned cylinder head has been used. The system was mechanically controlled and there were a lot of technical problems with it.
In the late 1970s, the Ford Motor Company developed a stratified direct injection system, the engine was called "ProCo" and used a unique high-pressure pump and direct injectors. At least one hundred and fifteen Crown Victoria V8 cars were built by Ford in Atlanta, Hapeville. The project was suspended for technical reasons as the electronic control systems were still very primitive and the costs of pumps and injectors were very high. There were also problems with the emission of nitrogen oxides exceeding the standards of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The three-way catalyst used later also turned out to be an expensive solution.
In 1996, the first electronic gasoline direct injection appeared. A system developed by Mitsubishi The first application was the GDI engine in the 1.8L Mitsubishi Galant / Legnum 4G93, which was then brought to Europe in 1997 in the Mitsubishi Carisma. In Europe, due to the stringent standards, the problem of exhaust emissions emerged, and fuel consumption was higher than expected. In 1997, GDI's first six-cylinder engine appeared, the 6G74 3.5L V6. Mitsubishi has adopted this technology widely and has already produced over one million GDI engines.
In 1997, the Nissan Leopard VQ30DD with direct injection appeared.
In 1998 Toyota developed its D4 direct injection system and it appeared on a variety of vehicles in the Japanese market in the SZ and NZ engines. Toyota later introduced its D4 system to the European markets of the 1AZ-FSE engine in 2001 on the Avensis model. The Lexus GS 300 with the 3GR-FSE engine entered the US market in 2005. In the 2GR-FSE V6 engine, Toyota uses a more advanced direct injection system that combines both direct and indirect injection with two injectors per cylinder, a traditional indirect fuel injector (low pressure) and direct fuel injection (high pressure) in the familiar D4 system.
In 1999, Renault introduced the 2.0 IDE (Essence Direct Injection) on the Megane. Instead of a lean mixture, Renault used high exhaust gas recirculation rates to improve efficiency at low engine loads, while direct injection concentrates the fuel mixture around the spark. The GDI technology was sold by Mitsubishi to PSA Peugeot Citroën, Hyundai and Volvo.
In 2000, the Volkswagen Group unveiled its own direct injection gasoline engine in the Volkswagen Lupo 1.4 L (FSI). The technology was adapted from the Audi Le Mans R8 racing prototype. The Volkswagen group uses direct injection in its 2.0 l turbo-charged and naturally aspirated FSI. Later, 2.0L units were introduced in 2003 for the Audi A4 model. PSA Peugeot Citroën presented its first GDI (HPi) engine in 2000 with the Citroen C5 and Peugeot 406. It was a 2.0-liter, 16-valve EW10 D with 140 hp (104 kW), the system was manufactured under license from Mitsubishi.
In 2002, the Alfa Romeo 156 direct injection engine, JTS (Jet Thrust Stechiometry), appeared, this technology is now used in almost every Alfa Romeo engine.
In 2003, a new 1.8 L Duratec SCi naturally aspirated direct injection engine appeared in the Ford Mondeo.
In 2003, BMW introduced a low pressure direct injection system for the N73 V12 engines. In 2006, the second generation of High Precision Injection (HPI) was introduced on the new turbocharged N54, which used high-pressure injectors. PSA is working with BMW on a new line of engines that debuted in 2007 in the MINI Cooper S. Honda has released its own direct injection system sold in Japan where the injector is placed directly on top of the cylinder at right angles, not sloping ones.
In 2004, General Motors released three direct injection engines: a 155 hp (116 kW) 2.2 L Ecotec version used in the Opel / Vauxhall Vectra and Signum in 2005, a 2.0 L turbocharged Ecotec in the new Opel GT. In 2004, Isuzu produced the first GDI engine. The Renult company withdraws from the production of IDE engines, the official reason is the difficulty in meeting exhaust gas purity standards, in particular NOx, and unofficially because of problems with the failure rate of power units.
In 2005, Mazda introduced its own direct injection version on the MAZDASPEED6 and later on the CX-7. It is known as Direct Injection Spark Ignition (DISI).
In 2006, BMW released a new version of the N54 twin turbo engine for its 335i Coupe, and later the 335i Sedan, 535i series and 135i models. Mercedes-Benz has developed CGI direct injection for the 350 CLS CGI, piezoelectric direct injectors have been used. The CLS 350 CGI offers 292 BHP
In 2007, Ford introduced its new Ford EcoBoost with engine technology for a variety of global vehicles (from small to large trucks). The engine first appeared in 2007 on the Concept Lincoln MKR under the name TwinForce
In 2008, the BMW X6 xDrive50i launched the Twin Turbo N63 V8 direct injection engine.
In 2009, Ferrari started selling the California direct injection model and announced that its new 458 Italia would also be equipped with a direct injection system. Porsche also began selling the 997 and Cayman equipped with direct injection. Ford has produced the next-generation Taurus SHO and Flex with the 3.5 L twin-turbo EcoBoost V-6 direct injection. Holden also added two direct injection engines for the V6 Commodores variant under the name sidi or Direct Injection Spark Ignition.
In 2010, Infiniti will produce the M56 direct injection engine. Motus Motorcycles develops the Katech KMV4 direct injection engine for the drive of MST motorcycles. 2011 Hyundai Sonata introduces the model with the GDI engine, including the turbocharged 2.0-liter with 274 hp.
By 2014, all Mazda engines will use SkyActiv direct injection, meaning all new Mazda vehicles will be equipped with GDI after 2014.